Categories
Categories
- Home
- General
- General 1950-present
- Monsanto Company bond 1977 (biotech and agriculture)
Monsanto Company bond 1977 (biotech and agriculture)
Product Description
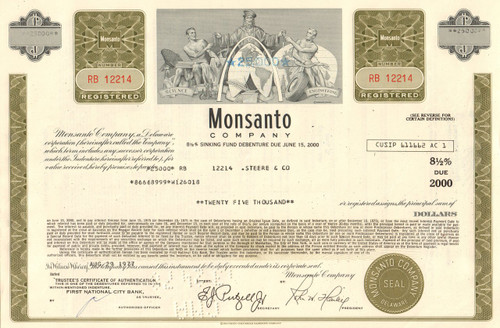
Monsanto Company bond certificate 1977 (biotech and agriculture)
Nice agricultural collectible. Great vignette of classical male figures around a map of the western hemisphere with wheat stalks and the word Science and Engineering. Issued and cancelled. Blue stamp into vignette of the bond dollar amount. Dated 1977
Monsanto Company is a publicly traded American multinational agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation headquartered in Creve Coeur, Greater St. Louis, Missouri. It is a leading producer of genetically engineered (GE) seed and Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide. Monsanto's role in agricultural changes, biotechnology products, lobbying of government agencies, and history as a chemical company have made the company controversial.
Founded in 1901 by John Francis Queeny, Monsanto initially produced food additives, expanded into industrial chemicals like sulfuric acid and PCBs in the 1920s. By the 1940s, it was a major producer of plastics, including polystyrene and synthetic fibers. The company also formerly manufactured controversial products such as the insecticide DDT, PCBs, Agent Orange, and bovine growth hormone.
Monsanto was among the first to genetically modify a plant cell, as one of four groups announcing the introduction of genes into plants in 1983, and was among the first to conduct field trials of genetically modified crops, which it did in 1987. It remained one of the top 10 U.S. chemical companies until it divested most of its chemical businesses between 1997 and 2002, through a process of mergers and spin-offs that focused the company on biotechnology.
Monsanto was one of the first companies to apply the biotechnology industry business model to agriculture, using techniques developed by Genentech and other biotech drug companies in the late 1970s in California. In this business model, companies invest heavily in research and development, and recoup the expenses through the use and enforcement of biological patents.
Monsanto was started in St. Louis, Missouri, in 1901 as a chemical company, by John Francis Queeny, a 30‑year veteran of the pharmaceutical industry. The company's first products were commodity food additives, like the artificial sweetener saccharin, caffeine, and vanillin. Monsanto expanded to Europe in 1919 by entering a partnership with Graesser's Chemical Works at Cefn Mawr, near Ruabon Wales, to produce vanillin, aspirin and its raw ingredient salicylic acid, and later rubber processing chemicals. In the 1920s Monsanto expanded into basic industrial chemicals like sulfuric acid and PCBs. Queeny's son Edgar Monsanto Queeny took over the company in 1928. In 1926 the company founded and incorporated a town called Monsanto in Illinois (now known as Sauget). It was formed to provide minimal regulation and low taxes for the Monsanto chemical plants at a time when local jurisdictions had most of the responsibility for environmental rules.
In 1946, Monsanto developed and marketed "All" laundry detergent until they sold the product line to Lever Brothers in 1957. In 1947, its styrene factory was destroyed in the Texas City Disaster. In 1949, Monsanto acquired 'American Viscose' from England's family business Courtaulds. In 1954, Monsanto partnered with German chemical giant Bayer to form Mobay and market polyurethanes in the United States. In 1964 Monsanto chemists invented AstroTurf (but called ChemGrass), which the company then commercialized. In the 1960s and 1970s, Monsanto was one of the most important producers of Agent Orange for United States Armed Forces in Vietnam. In 1985, Monsanto acquired G. D. Searle & Company, a life sciences company focusing on pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and animal health. In 1993, Monsanto's Searle division filed a patent application for Celebrex.
In 1996, Monsanto purchased Agracetus, the biotechnology company that had generated the first transgenic varieties of cotton, soybeans, peanuts, and other crops, and from which Monsanto had already been licensing technology since 1991. Monsanto first entered the maize seed business when it purchased 40% of DEKALB in 1996; it purchased the remainder of the corporation in 1998. In 1998 Monsanto purchased Cargill's international seed business, which gave it access to sales and distribution facilities in 51 countries. In 2005, it finalized the purchase of Seminis Inc, a leading global vegetable and fruit seed company, for $1.4 billion. This made it the world's largest conventional seed company at the time. In 2007, Monsanto and BASF announced a long-term agreement to cooperate in the research, development, and marketing of new plant biotechnology products.
Product descriptions and images
Please note that some pictures may only be representative of the inventory available. If we have more than one piece, we are unable to scan and display every piece. Unless otherwise noted, that there are variations for signatures, cancellation marks/holes, serial number, and dates. Colors will be as noted and pictured.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...